← Back to the list of articles
Biometric Technologies in Video Surveillance with Xeoma: Features and Security
TL;DR: Biometric technologies in Xeoma are tools for identification by face, voice, emotions, and behavior. Supports 99% of cameras, works on any OS, includes face recognition with 90% accuracy, fall detection, mask detection, and speech recognition. Used in healthcare, access control, and research. Simple setup: download Xeoma, configure modules. Free trial period available for any functionality.
| Ready to implement biometrics in video surveillance? Download Xeoma for free from the official website and start now! Download Xeoma |
What is Biometrics and Why is it Important in Xeoma
According to Wikipedia, biometrics is the measurement of physical and behavioral characteristics of an individual. While the term “biometrics” refers specifically to a set of human characteristics, in the modern world it is primarily used in the context of biometric authentication, i.e., either the ability to identify a person by various biometric parameters or the identification process itself. Notably, the term originally applied only to humans, but it is not uncommon for it to be used in a figurative sense for other animate or even inanimate objects. In this article, we will focus on humans.
“Biometric authorization” may sound highly technological or even futuristic to some, but in reality, many of us are familiar with it—directly or indirectly, observing others using it daily. Mobile phones that unlock with a glance at the camera or a fingerprint scan are a perfect example of how biometric algorithms look and work.
Why are biometric security measures important? Primarily, they represent a modern multifactor method of verifying a person’s identity, addressing many shortcomings of older methods, such as password or ID-based authorization. Biometrics is a collective term that can encompass entire combinations of characteristics relevant to a particular field or situation. People tend to forget passwords or lose identification documents (or they can be stolen), and IDs are often left at home. Not to mention fraudsters whose activities rely on extorting data or documents from unsuspecting victims for their own gain. Biometrics is harder to steal and impossible to lose.
How Video Surveillance Relates to Biometrics: Xeoma Capabilities
What do biometric security and security cameras have in common? Security! Essentially, video cameras, without which surveillance systems are unimaginable, are another means of collecting biometric data. Surveillance cameras can be seen as specialized equipment for gathering biometric information, standing alongside fingerprint scanners or heart rate sensors. Naturally, this is why biometrics and video surveillance intersect in several areas, one of the largest being access control in its broadest sense. In a way, access control is a primary task for both video surveillance and biometrics: one of the most common uses of video surveillance in everyday life is intrusion detection, which is essentially preventing unauthorized access to restricted areas—a form of access control. As for biometrics, the term originated in connection with access control, as biometric identification allows people to access services, facilities, websites, or devices. Biometrics collected by cameras is one of the tools that video surveillance uses for access management. In other words, video surveillance is one of the methods for collecting biometric data.
The same logic applies to personnel management—another area where biometrics and video surveillance go hand in hand. The reason may be that personnel management is, in a sense, another form of access control, where it’s not only important to recognize whether a person is allowed on the premises but also to track their activity and productivity using collected data.
Another field where biometrics and video surveillance work together is scientific research. In many experiments, scientists use biometrics to distinguish subjects during data collection; however, the results are often anonymized, as only the fact of discovery matters. In this field, surveillance cameras also serve as collectors of biometric information, relying on computer vision for reading emotions, attention direction, demographic data, and more. In marketing research, for instance, this combination can identify which products, advertisements, or product placement zones generate the most profit—or provide insights into the demographic characteristics of the customer base. Scientific research typically focuses on studying human behavior or psychology. Instead of undergoing supervised examinations where results are monitored and recorded by someone else, interaction with cameras feels less personal and intrusive, allowing people to exhibit genuine reactions.
A significant advantage of video surveillance is its multifunctionality. Many companies start using video surveillance for collecting footage and alerting security personnel upon intrusion detection, but soon discover a completely new level of video analytics capabilities. After all, if cameras are already installed for security purposes, why not unlock their full potential?
| Xeoma supports 99% of cameras on the market, including 430+ brands, for accurate data collection. Check your camera’s compatibility with Xeoma: List of supported cameras |
Biometric Technologies in Xeoma: Face Recognition, Voice, and More
We’ve mentioned that surveillance cameras sometimes use biometric identification. But which specific types of biometrics can they work with?
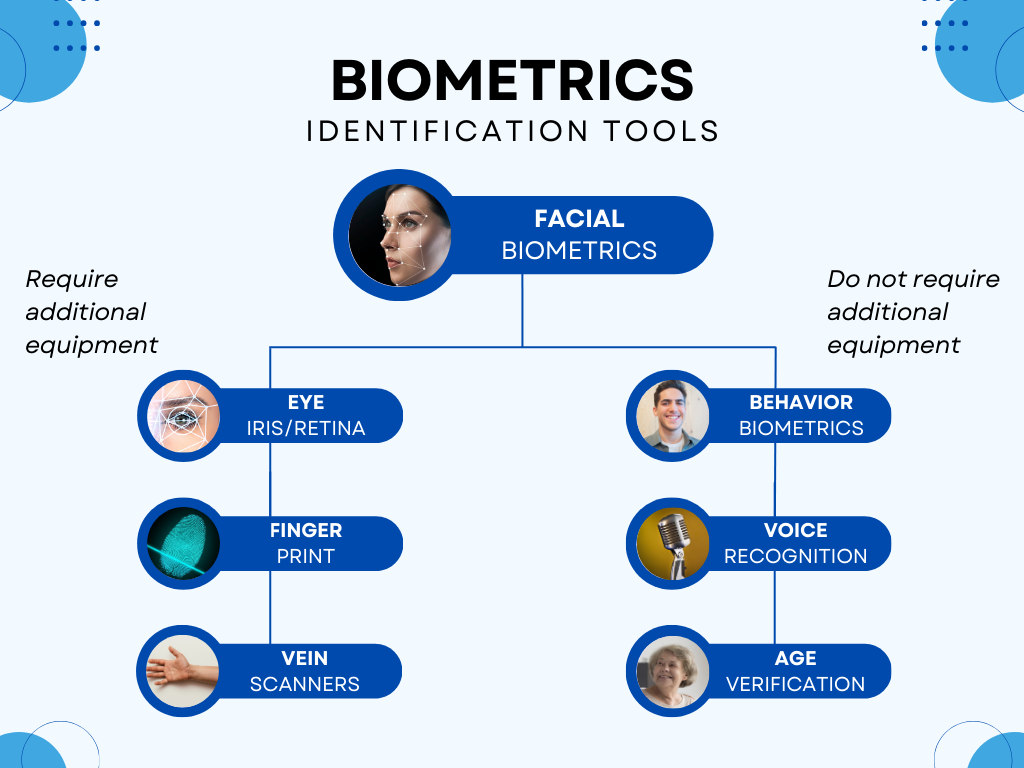
First and foremost, facial biometric data, which surveillance systems collect using a specialized tool called “Face Recognition”. Cameras transmit real-time video streams to advanced intelligent software, which then detects a person in the image, scans their face, and remembers unique features to recognize the same person upon reappearing in the frame. Technically, this process is almost identical to face recognition in smartphones, with the difference that surveillance can handle hundreds or thousands of faces, not just one. A person’s face is a universal biometric parameter applicable to any field requiring identification. And since we’re on the topic, it’s worth mentioning the eye scanner, capable of recognizing the retina or iris of the eye—another unique part of the human body.
While facial biometrics may seem like a self-sufficient identification tool, modern systems use it in combination with other biometric features to provide more effective fraud protection. For example, liveness detection aims to identify situations where fraudsters place photos or videos of people, found on social media or even generated by neural networks, in front of the camera. In video surveillance, the primary means of liveness detection is the motion detector, designed to respond only to the movement of an object in the camera’s field of view. In addition to this and other “external” surveillance tools that can also be used for presence detection (e.g., from the “Loitering Detector”), there are also anti-fraud technologies built into access control tools (e.g., Face ID, which we’ll discuss below).
Age verification is another AI-based mechanism that can be used in conjunction with facial biometrics for double protection against breaches of various security protocols. By comparing the age of a person attempting to access a service with the age listed in their account, fraudsters lacking access to accurate information or means to reproduce it can be deterred. Modern video surveillance solutions like Xeoma provide various tools for demographic data analysis, including recognition of gender and age, which can be used separately or together for various purposes.
Voice biometrics is another type of enhanced protection against malicious actors attempting to access a person’s account. Voice control is gaining unprecedented popularity, whether for household interactions with smart home stations like Alexa or for conducting banking operations. Working with sound is hardly within the duties of the all-seeing eye of video surveillance, but advanced solutions like Xeoma offer capabilities for working with audio streams: these include, for example, “Sound Event Recognition”, capable of identifying the type of sound, or “Speech Recognition”, which can convert spoken words near the camera or even call recordings made elsewhere into text.
When it comes to a biometrics-based anti-fraud complex, we shouldn’t forget behavioral biometrics. Its presence implies that a person can be identified by how they act, move, or even feel. The range of required unique traits is quite broad: from gait to predominant mood. Surveillance solutions with intelligent video analytics typically feature a specialized tool called “Emotion Recognition”, aimed at reading a person’s mood from their face in the frame. For example, Xeoma’s “Face Detector (Emotions)” module is trained to recognize seven emotions and their combinations on faces in the camera’s field of view.
Above, we listed the main “players” in biometric identification systems, but there are certainly other biometric parameters that can be used for the same purposes—either alone or in combination with those described earlier.
Biometrics and Video Surveillance in Healthcare with Xeoma
Healthcare is a broad term encompassing a wide range of institutions: clinics, nursing homes, rehabilitation centers, diagnostic laboratories, and many others. Each of these organizations faces unique challenges requiring tailored solutions. Biometric authentication is among these solutions. Biometric authorization mechanisms are rapidly transforming access control, personnel and patient management, and compliance with regulatory requirements in medical institutions.
Ask someone to list traits unique to any person. Most will mention DNA, dental records, or fingerprints. Fingerprint recognition, for example, is a leading authorization method for digital healthcare services (such as online consultations on specialized websites), at least because it finds new applications for scanners and similar technologies pre-installed in modern smartphones. In-person fingerprint authentication requires specialized equipment, installation, and maintenance, but it can be used to grant access to restricted areas or confidential patient files, offering a modernized replacement for traditional IDs—more reliable and harder to lose or forge. However, with growing public awareness of hygiene and infection control requirements, contactless biometric methods are gaining popularity—a safe alternative ideal for sterile environments (e.g., surgical wards or laboratories) or situations where hands are simply occupied.
Facial biometrics, another key biometric analysis tool, has found widespread use in healthcare due to its efficiency and adaptability. Patient identity verification during registration (or even upon entering a website!), restricting access to secure areas—face recognition offers a seamless and contactless solution for these and many other situations. Xeoma’s “Face Recognition” module speeds up this process, adds reliability, and eliminates the need for additional equipment—only a video camera is required. Users note a 70% reduction in false positives thanks to smart algorithms.
It may seem that another tool—eye recognition, based on scanning the iris or retina of the eye—would be a logical continuation of facial identification methods, but such scanners are costly, affordable only by top-tier security systems, while face recognition performs roughly the same functions.
Similarly, voice biometrics, analyzing speech patterns for individual identification, behavioral biometrics based on actions, or age verification can be used as a second layer of protection in digital authentication. Age recognition through biometric analysis also ensures appropriate treatment plans and compliance with age-related protocols. Specifically for such tasks, video surveillance provides tools like “Age Recognition”—often an indispensable component of comprehensive demographic analytics solutions. Another advantage of the Xeoma video surveillance software is the presence of the “Speech Recognition” module, which can be configured to respond to specific words or phrases, such as “Yes,” “No,” or a designated password—and then used as a complement to biometric authorization, especially when interacting with patients or processing calls in a call center.
Sometimes, medical institutions need to identify a person without using the above tools—especially in emergencies when patients are brought in by ambulance. When a person is unconscious, disoriented, or simply unable to speak or move, voice or behavioral recognition is impossible. Progressive medical organizations may use vein scanners to access such a patient’s medical history—for example, to immediately determine allergies to a drug that needs to be administered. Another exciting aspect of surveillance systems like Xeoma is their ability to integrate with third-party technologies and devices—like vein scanners—for ultra-secure, non-invasive, and sometimes life-saving patient identification. Integration with wearable biometric devices, for instance, allows real-time monitoring of a patient’s health metrics: heart rate, oxygen levels, and more—which can be visualized directly in the surveillance system’s interface for quick response to detected ailments. By seamlessly working with third-party technologies, surveillance systems can serve as centralized platforms, combining physical security, health monitoring, and efficient handling of all necessary information, fostering a cohesive and productive healthcare environment.
The world we live in changes regularly—there’s often not enough time for waiting for an appointment or traveling to a hospital. That’s why biometrics is increasingly integrated into websites offering healthcare and telemedicine services. Tools like face recognition and fingerprint scanning enhance the reliability of registration portals, ensuring secure system login and access to confidential medical data. Voice biometrics optimizes virtual consultation processes and call center support systems, offering patients with limited mobility voice-based identification capabilities, as well as providing staff with the ability to record expressed complaints and suggestions for later review. Behavioral biometrics analyzes patterns like typing rhythm or mouse movements to provide continuous, unobtrusive authentication and liveness verification during online sessions. Thanks to these technologies, healthcare services become safer, more efficient, and more accessible, further emphasizing the importance of biometrics in modern healthcare.
The variety of modules in Xeoma goes beyond biometrics to enhance security protocols, workforce productivity, and patient care quality in medical institutions. The “Fall Detector” recognizes falls in real-time, ensuring immediate response to prevent serious injuries in facilities like nursing homes and rehabilitation centers. The “Mask Detector” ensures compliance with mask-wearing requirements during infectious disease outbreaks, protecting both patients and hospital staff. The “Thermal Camera Integration” allows automatic alerts upon detecting fever in patients or staff. Various visitor counting methods in Xeoma help manage guest and staff flow, ensuring patients receive adequate attention and care, thereby improving accountability and service quality. Moreover, Xeoma’s innovative “Heart Rate Monitor”, currently in development, is set to revolutionize patient monitoring by non-invasively tracking stress levels and potential health threats. All these tools, combined with the program’s advanced video analytics capabilities, ensure that Xeoma is a positively comprehensive solution tailored to meet the unique needs of medical institutions.
Using the healthcare industry as an example, we’ve demonstrated how biometrics and video surveillance can form a symbiotic ecosystem, but this result can certainly be observed in other scenarios and niches: private, security, research—be it scientific or marketing. Innovations in surveillance systems can significantly enhance physical security systems while optimizing any business’s operations through cutting-edge intelligent video analytics solutions, making them indispensable assistants in both private and professional modern environments.
|
Buy a Xeoma license at a great price and implement biometrics. Contact tech support for consultation! Xeoma Tech Support Buy License |
FAQ
- What is biometrics in Xeoma?
- It is identification by face, voice, emotions, and behavior using AI for security and access control.
- How to set up face recognition in Xeoma?
- Add the “Face Recognition” module, upload a face database, configure reactions (notifications, access).
- What biometric functions are available in Xeoma?
- Face, emotion, age, gender, and speech recognition, among others.
- How much does Xeoma with biometrics cost?
- License from Standard + Additional modules, with free trial; details on the website.
- Does Xeoma support speech recognition?
- Yes, the module converts speech to text for analysis and reactions.
February 19, 2025, updated September 8, 2025
Read also:
Video Surveillance Solutions for Other Industries and Sectors
Video Surveillance and Analytics in Access Control Systems (ACS)
Video Analytics in Xeoma
Xeoma Additional Modules Based on Artificial Intelligence
Learn More About Face Recognition in Xeoma
Setting Up Notifications in Xeoma: Detailed Instructions
Compare Xeoma with Competitors