How to work with artificial intelligence for better results

In recent years, neural network technologies have been rapidly gaining momentum, making giant leaps in development. The higher the quality of artificial intelligence (often called simply AI), the more industries begin to use it for solving a wide range of tasks. However, it’s no secret that AI is still artificial intelligence, so to achieve quality results, you need to know how to work with it and carefully analyze outputs generated by neural networks. Whether a student is writing a thesis or a programmer is using a neural network to help write code, the consequences of an error can be, at the very least, unpleasant, – and for areas related to security, downright catastrophic. Let’s explore whether AI makes mistakes and how to work with artificial intelligence for better results.
PART 1. DOES AI MAKE MISTAKES?
In short, yes, AI absolutely makes mistakes. This is confirmed by the now-infamous meme-worthy examples of artificial intelligence struggling to generate images of people with the correct number of fingers. Ask a neural network for help with translation, and without proper oversight, it will likely mess up the tone or word choice. Ask it to compile a list of suitable job openings, and a professor might well be offered a position as a chef. Use artificial intelligence to classify objects, and it’s quite possible that under certain conditions, it will mistake a cat for a dog. Try dictating a text, and instead of texting someone they are “pleasant” you have all chances to accidentally call them a “peasant”. Generated photos and posts by artificial intelligence are still relatively easy to distinguish from real ones, not only due to characteristic details but also due to characteristic errors.
For those who regularly work with neural networks, the question isn’t “Does AI make mistakes?”. The real question is: how do you prevent AI from making mistakes, how do you work with artificial intelligence for better results? To answer this question, you need to understand how AI actually works. We’ll explore that in the next chapter.
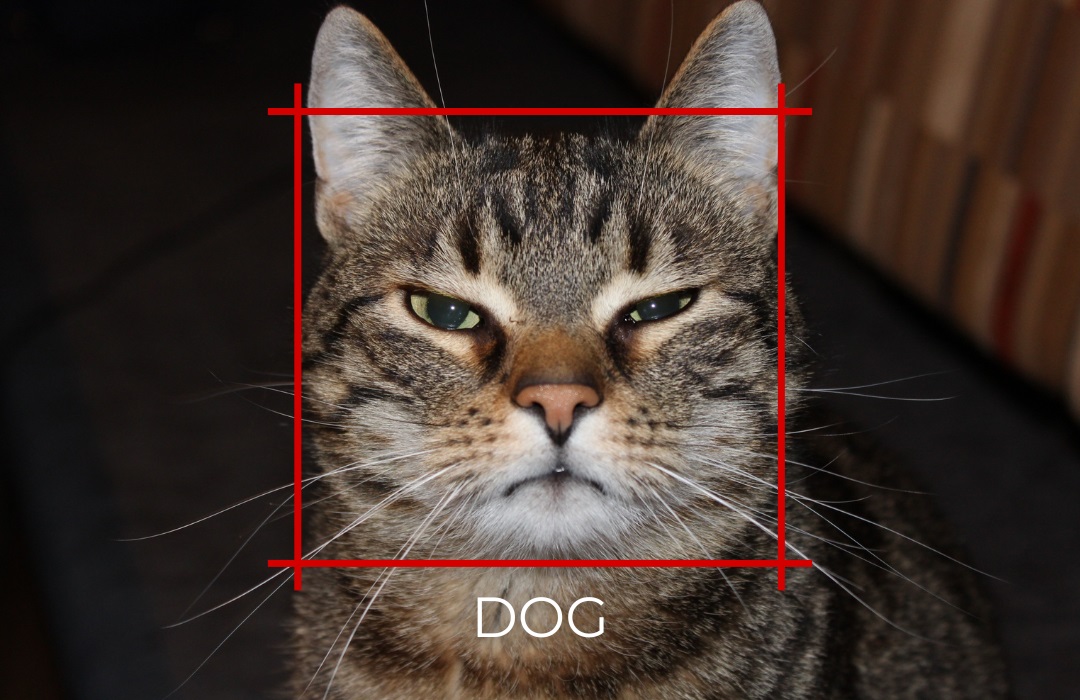
“Soon AI will take over the world”. AI at the same time:
|
PART 2. HOW DOES ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE WORK?
If we take a philosophical approach, artificial intelligence in many ways mirrors human intelligence: it’s a combination of theory, numerous examples we call experience, and assumptions. For example, how does a person understand that they are looking at an apple? We judge by the appearance, smell, and shape of the object and compare it to what we already know about apples, and how apples have looked in real life, in books, on TV, and so on. And if something doesn’t match, we start extrapolating: “If this isn’t an apple, then what is it?”
Artificial intelligence works the same way. It knows about objects based on the materials it was trained on or the data it has real-time access to. Typically, a neural network is trained on massive datasets, unimaginably large sets of examples, often taken from the Internet. And AI’s out-of-the-box performance depends entirely on the quality of these materials, which in today’s world, full of contradictory information and fakes, can be a problem.
So, what can be done to improve the quality of AI’s outputs now that we know how it works?
PART 3. GETTING THE MOST OUT OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Considering everything we’ve talked about, there are two main ways to tinker AI for better results.
1. Be incredibly specific with your instructions – what’s known as “prompting”. Clearly tell the AI exactly what you want it to do, and just as importantly, tell it what you do not want it to do. For research, ask it to stick to verified sources and back up its claims. When creating content, don’t skimp on detail – describe not just what should be in the final product, but also what you want to avoid.
2. Train the AI yourself using high-quality materials. Some AI companies now let you independently train their neural network. A business could “feed” its website to the AI and create a chatbot that helps visitors find information – and ideally, get direct answers to their questions. The biggest challenge here? You’ll need some serious computing power. Currently, training and running a ‘local’ version of AI on your own infrastructure requires powerful hardware, which can be expensive for individuals – and even some companies.
There’s a third, less famous approach, particularly relevant for applications like video surveillance: choose those manufacturers and products that are widely known for their robust training processes. This article set to highlight independent use of AI language models, but it’s good to remember that AI is more than that: AI technologies can be integrated into programs and applications that develop and train neural networks themselves. Video surveillance systems like Xeoma, for example, use AI for object, person, event, and sound recognition, to do which the manufacturer has trained the neural network with lots of real-world examples – photos, videos, audio – to ensure better results. Besides, with Xeoma you can request custom adjustment or retraining of the selected tools to match with your specific cameras and needs.
But that’s not all! Advanced artificial intelligence solutions like that allow you to get the best performance, not just by relying on the expertise of the developers, but also through intelligent configuration. We’ll explore that in more detail below.
PART 4. RIGHT SETTINGS FOR BETTER RESULTS
The best software products aren’t just well-trained; they also give you control over how the AI performs.
Xeoma is a great example. It started off as a video surveillance program, but now offers tools beyond the security scope – ones aimed to optimize and automate business processes. It includes dozens of advanced video analytics features – from detecting people to converting voice to text and responding to specific “events”. Typically, each such event or object that we’d like AI to ‘recognize’ has specific requirements that must be minded for precise results. However, there are some general best practices, too! For example, to accurately recognize animals, the video camera needs a clear view. When it comes to microphones, in order to accurately recognize speech, position the microphone close to the sound source and minimize background noise. Some features also have specific hardware requirements. Xeoma’s double authentication works on most operating systems, but the helmet detector requires a 64-bit system, while the fall detector and restaurant visitor counter require specific processors to function.
However, the ways to properly configure AI-powered functions don’t end there! As we mentioned before, every “object” you’re trying to detect has its own unique characteristics, and each tool designed to work with that object will reflect those characteristics in its requirements. For example, license plate recognition has a minimum size for the plate that Xeoma can reliably process, while people counting in a queue detector requires a specific viewing angle that allows it to see heads, and fire detection works best with a contrasting background.
Most modules in Xeoma also have internal settings you can adjust to help AI yield better results. Text recognition lets you choose a model, ranging from simple and fast to highly accurate but resource-intensive. License plate recognition lets you specify the country or countries you need it to read. Face detection lets you set a distance at which it should start looking for faces, preventing it from wasting time analyzing objects that are just too distant.
That brings us to a question, ‘How do I actually configure artificial intelligence for better results?’ Luckily, Xeoma has you covered in that respect, too! First, check the settings within your tool of choice – they usually contain helpful information and tips. Xeoma also offers a comprehensive user manual and dedicated articles and videos on configuration of its features, including, of course, intelligent ones. Still stuck? Xeoma’s responsive technical support team is always happy to answer your questions and recommend the best solution. Plus, a lot of work has been done by Xeoma devs to make the program and its components perform reliably out-of-the-box, while also being intuitive to use. It enhances a good chance of figuring things out without external resources even for beginners.

Recommended camera position for video analytics in Xeoma video surveillance software
|
As you can see, the answer to “Does AI make mistakes?” is fairly straightforward. But the answer to “How to work with artificial intelligence for better results?” requires a more personalized approach, as the solution depends on the specific AI tool. For example, Xeoma’s video surveillance and problem-solving software boasts over 30 intelligent video analytics functions, all of which can (and should) be configured in an optimized way, taking their unique characteristics and purpose into account, to get better outputs.
However, if you prefer a hands-on approach, another good news is that you can try out all of Xeoma’s AI capabilities for free! That’s right, Xeoma proudly serves the “Try before you buy” policy which allows you to test the solution before you commit. For example, to get a free demo license of Xeoma full version with over 100 features, simply use the form below!
Try Xeoma for free! Enter your name and your email to send the license to in the fields below, and click the ‘Get Xeoma free demo licenses to email’ button.
We urge you to refrain from using emails that contain personal data, and from sending us personal data in any other way. If you still do, by submitting this form, you confirm your consent to processing of your personal data
23 May 2025
Read also:
AI in Xeoma to detect suspicious behavior
Artificial Intelligence to the rescue: how video analytics helps solve business tasks
Intelligent video surveillance: how AI technologies are changing security
Additional modules in Xeoma